Strategic management at PTC (T-Mobile Polska)
Case study
Polska Telefonia Cyfrowa started its operations in 1996, taking advantage of the possibility of launching mobile telephony in the GSM900 system. The second half of the 1990s was a period of rapid development of ICT technologies and high demand for the services of mobile network operators. Developing business in this sector did not require any particular strategy at the time. There was enough space on the market and the only objective for each of the three existing operators was to attract as many customers as possible, ie to gain the largest possible market share. The product at the time was simple: cordless telephone plus voice calls, offered in several tariff plans.
The business grew very fast, but so did the competition. In addition to the call connection service, text messages and wireless broadband data transmission appeared. The leaps in technological progress opened up new possibilities, but at the same time posed an important question about how to use this potential. It was necessary to consider what services to offer in order to meet demand, increase sales and stay ahead of the competition. It became necessary to examine the needs of customers more and more precisely and carefully adapt the offer to the expectations of various market segments. As a consequence of the rapid growth, there was also a need to implement a strategic model of company management.
I participated in the creation and development of such a model, performing the duties of Deputy Head of Strategy, advisor to the President of the Management Board of PTC and Director of the PTC Business Development Office. I developed and implemented a strategic planning methodology, prepared and moderated strategic workshops for the top management and conducted strategic projects sponsored at the level of the PTC Management Board. I also participated as a mentor in the company’s coaching program, which involved sharing knowledge and experience with younger employees.
Strategic management in PTC practice
The strategic management system at PTC was introduced gradually as the young and fast-growing company matured. Basic business activities were carried out in the network management and marketing divisions, while supporting activities were located in the finance, administration and general director divisions. In such an organizational structure, business processes and procedures were systematically developed and optimised. One of the processes was the strategic planning process, which translated into procedures for cascading strategic goals and the daily practice of management by objectives, included in the intranet task programming and employee evaluation system. Project management procedures were also an important element of the strategic management model.
In addition to procedural and technical solutions, the implementation of the strategic management system required shaping the appropriate awareness of employees and organizational culture. In a turbulent business environment, in a situation of rapid technological, market and regulatory changes, current operational tasks pushed strategic thinking into the background. This was counteracted by strategic workshops organized for top management outside the company’s headquarters, as well as regular meetings of department directors with the Management Board of PTC. They were an opportunity to monitor the effects of activities on an ongoing basis and to learn a strategic approach to performing tasks at all organizational levels of the company.
SMART & KPIs
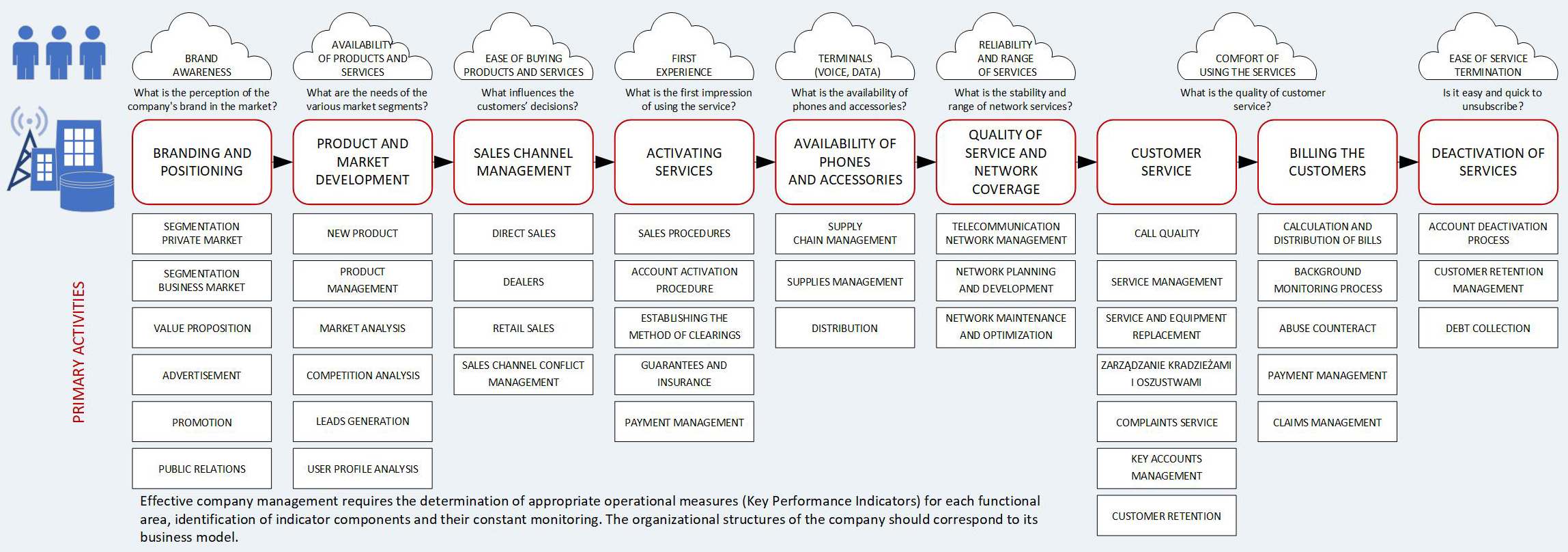
The essence of correct strategic planning is to set specific goals that should meet the requirements set out in the SMART principle, because: “You cannot manage something that cannot be measured” (Peter Drucker). Specification of goals is achieved through the use of performance indicators, i.e. KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).In mobile telephony, the following indicators are of primary importance: Customer satisfaction, Brand awareness, ARPU, EBIDTA, Market share, Churn rate, Bad debt, Customer acquisition cost, Employee satisfaction, and many others. Understanding structure fo KPIs is the fundamental condition for understanding the essence of the company’s business model and necessary for making the right decisions at the strategic, tactical and operational level.By describing strategic goals with indicators, it is possible to monitor the effects of the implementation of the established strategic plan on an ongoing basis and to make corrections quickly.
- Network operator model
- Structure of a business strategy
- Product life cycle
- Media convergence
The three most important words in any business are: “demand – product – supply”. The company’s activity is primarily to meet the demand on a specific market. Recognition of demand is associated with the need to study customer needs and create segmentation according to the adopted criteria. The two main market segments in the mobile telephony sector are the private market and the business market. On each of them, further sub-segmentation is made according to the specific criteria describing a specific group of people or institutions (e.g. according to the age of telephone users or the industry in which the company operates). Knowing the needs of individual market segments, it is possible to design appropriate products (telecommunication services) for each of them, i.e. to offer the so-called value for the customer. The ability to offer this value is associated with specific production requirements, i.e. the need to possess the appropriate technologies and qualifications.
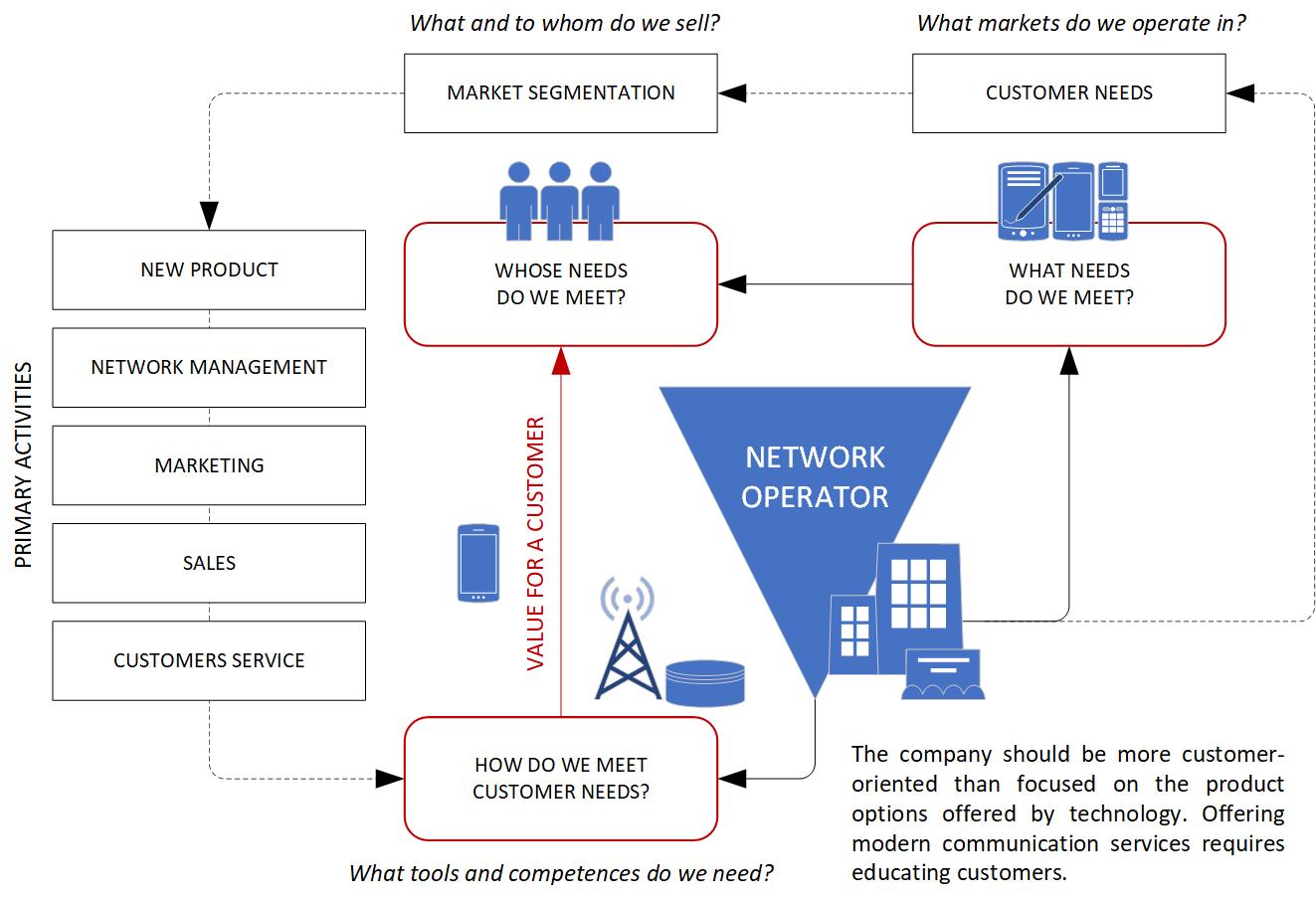
Telecommunications services are provided in a chain of basic activities, consisting of designing new services, implementing them in the network (IT systems), market communication (marketing), sales and after-sales service. The basic activities of the company are accompanied by supporting activities, such as financial, legal, HR and administrative services.
The starting point in strategic planning is the realization that the essence of a company’s business is meeting the needs of its customers and other stakeholders, not money. Sales revenues and profits are only a result of proper identification and satisfaction of market needs, as well as the expectations of employees, technology suppliers and authorities issuing licenses for the use of radio frequencies. Of course, stakeholder groups can be listed more. Good recognition of the company’s competitive environment is the basis for formulating a realistic vision of development, and then determining the corporate strategy, the strategy of individual business units and the strategy at the functional level of the company.
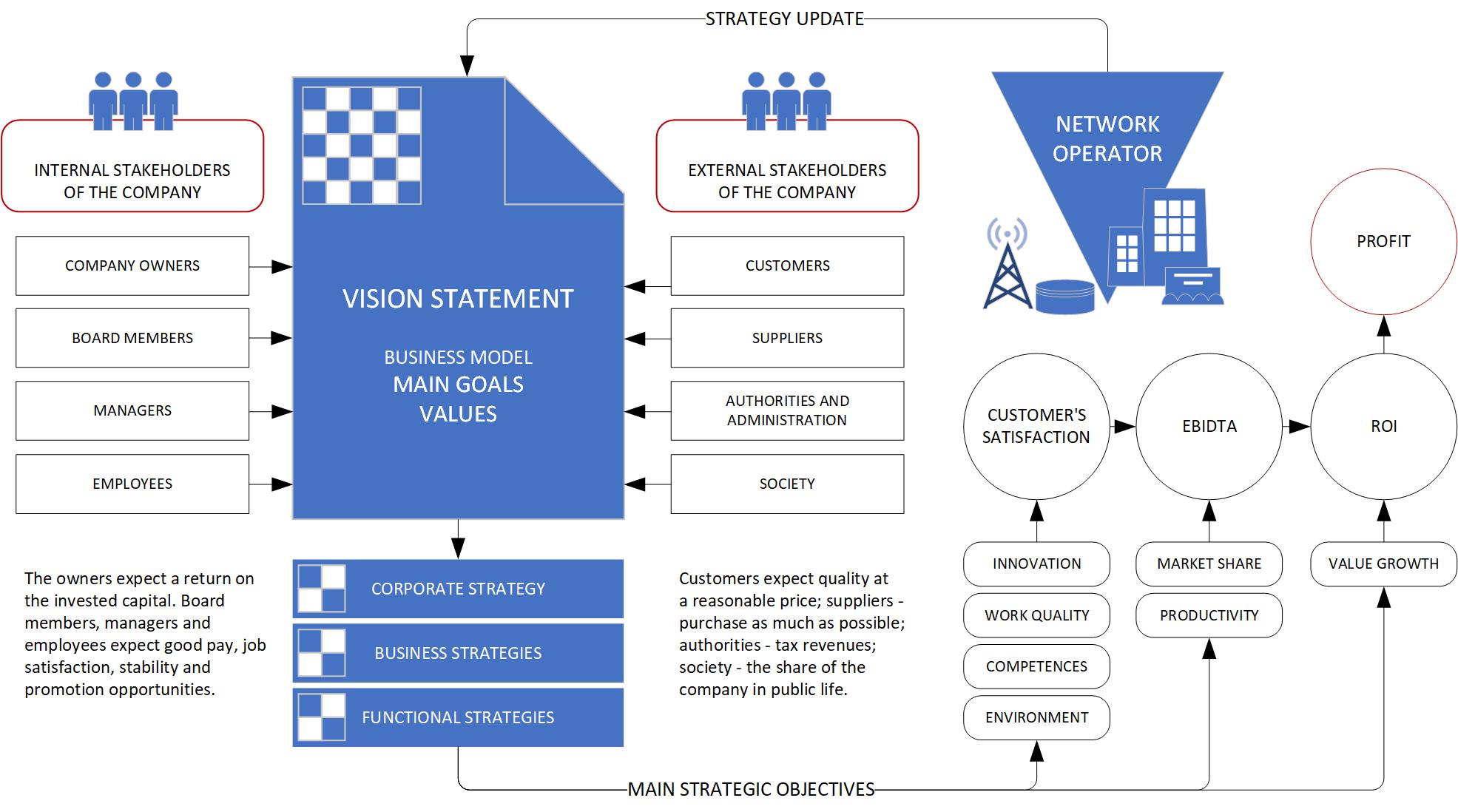
Every company that operates in free market conditions should strive to achieve the classic sequence of main strategic goals, i.e. the highest possible level of customer satisfaction, operating profit, return on investment and net profit. The ability to achieve these goals is determined by the creation of good working conditions, the acquisition of competent and ethical employees, the achievement of high quality and efficiency of work and the use of modern technologies.
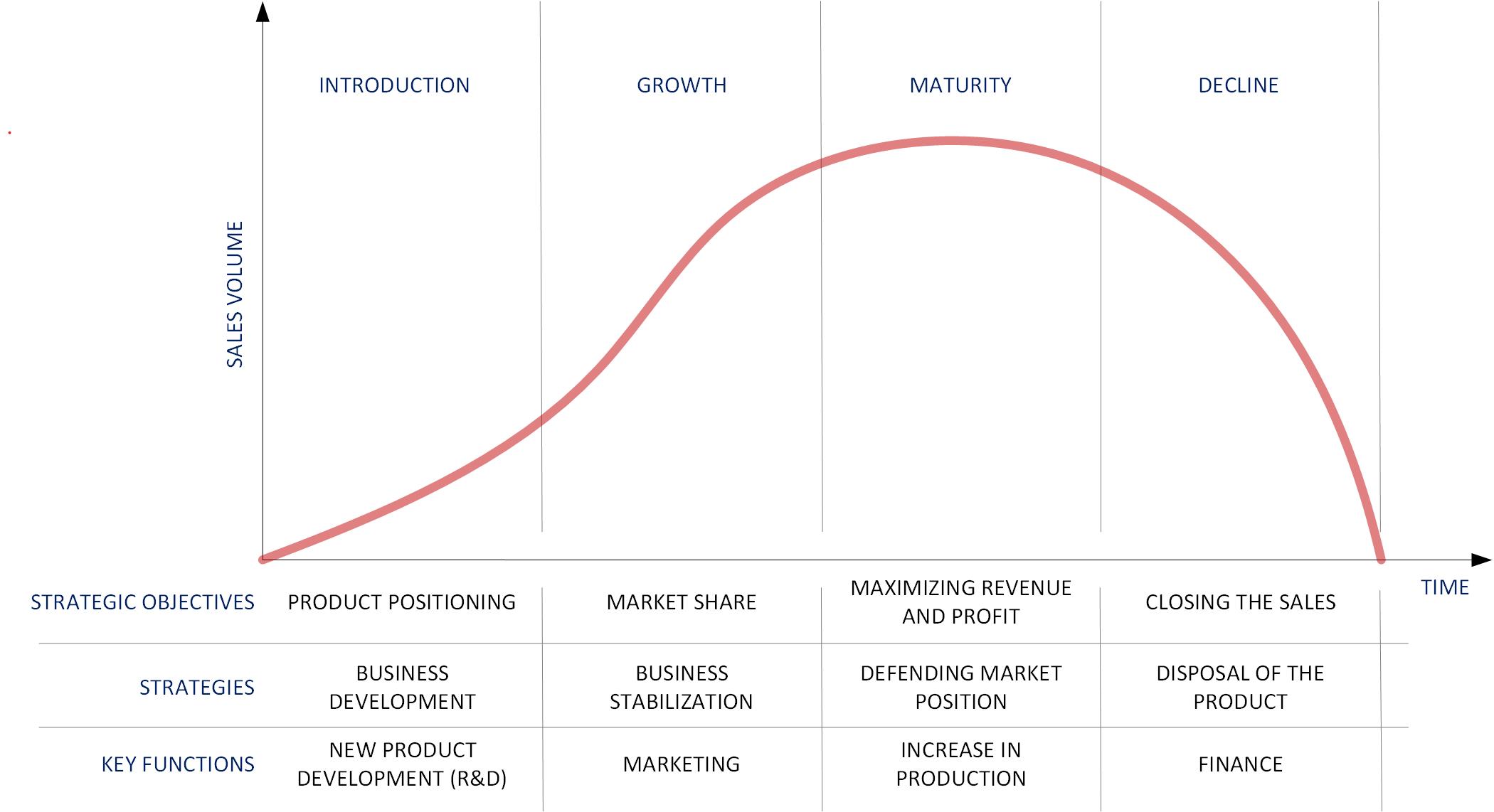
Most products have a specific time of their presence on the market, which can be divided into four phases: the phase of launching, the phase of growth, the phase of maturity and stabilization, and the phase of decline, i.e. leaving the market. The product life cycle is a natural consequence of the increase in sales and production, market saturation, the emergence of competitive products and technological progress. Old products and services are being replaced by new ones. Each phase of a product’s life can be assigned specific strategic goals and activities. Product Life Cycle Analysis is part of managing a product portfolio of which there is a great variety in the mobile telephony industry. The BCG Matrix, which divides product portfolios into four main categories: cash cows, question marks, rising stars and dogs, can be a great help in strategic management of telecommunications portfolios.
The concept of the product life cycle can also be applied to the analysis of industry life cycles. Life cycles (development) in the mobile telephony sector are determined by successive technological standards, from 1G telephony to 5G and 6G (in the meantime). We can analyze the periods of use of NMT, GSM, GPRS, EDGE, UMTS, HSDPA, LTE or 5G technologies in a similar way as the life cycles of individual telecommunications services.
The 20th century was a period of rapid development of communication technologies. The telegraph, telephone, radio, television and computer networks offered new possibilities for the transmission of information in all areas of life. The dissemination of the Internet and wireless telephony (cellular, satellite) in the 1990s greatly accelerated the pace of technological and civilizational development, affecting all areas of life. These were groundbreaking changes that initiated the process of convergence, i.e. the penetration of communication technologies and the merging of electronic media into one system.

The modern smartphone has become a multifunctional device combining telephone, radio, television and network terminal. However, not only ICT and radio technologies participate in the convergence process, but also providers of specialized electronic content and services, such as press and television publishers, banks and social networking sites. Convergence changes the interactions between technologies, but also the operating models of enterprises, public administration, schools and non-governmental organizations. It also changed the relationships among people.
The best way to predict the future is to create it.
Plans are just good intentions unless they immediately turn into hard work. Strategic management is not a set of tricks or a set of techniques. It is analytical thinking and engaging resources to act.
Peter Drücker
Strategic management objectives
The main goal of implementing a strategic management model is to achieve a competitive advantage over other companies operating in the same industry and to ensure the company’s long-term survival. The strategic approach to management allows the use of most resources (property, financial, organizational, human) to achieve results in all functional areas consistent with the company’s strategy. It allows for the identification of strategic resources (e.g. know how), and also triggers stronger motivation and commitment of employees who work better if they know the goals of the organization and see their role and the importance of their own work in the overall collective effort. This is facilitated by the implementation of a permanent strategic planning practice and the management by objectives (MBO) system.
Consistent practice of strategic management combines analytical, design and current operational activities into a coherent whole. It also makes us realize that nothing is given once and for all and is subject to repeated cycles of growth, maturity and decline. Similarly to the Product Life-Cycle, the existence of a company and an industry is also limited in time, especially one as sensitive to market, legal and technological changes as mobile telephony. Strategic analyzes of the company’s environment and its internal development conditions allow you to make the right decisions at the right time and ensure the company’s survival.